Keyword [Citywide Crowd Flows]
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Qi D. Deep spatio-temporal residual networks for citywide crowd flows prediction[C]//Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2017.
对于公共安全和交通管理而言,预测人群流动具有重要意义,但它受到事件、天气和区域间等复杂因素的影响,因此该篇论文提出一个基于深度学习的方法 (ST-ResNet, Figure 3)综合预测一个城市中各区域人群的流入 (inflow)与流出 (outflow) (Figure 1).


ST-ResNet基于时间和空间数据 (spatio-temporal data),对temprtaol closeness, period和trend 3阶段交通拥挤程度进行建模,并结合external factors对进行预测。论文基于两个数据集Beijing和New York City (NYC)进行实验,并与6个baseline进行对比。
- Mobile phone signal of pedestrians.
- GPS trajectories of vehicles.
1. Complex Factors
- Spatial dependencies. Region的inflow受到附近regions的outflow影响,甚至受更远的regions影响。同时region的inflow也会影响它自身的outflow.
- Temporal dependencies. Region的flows也受到近期时间段的影响。例如,8点的交通阻塞可能会影响到9点的交通情况;每个工作日的高峰期相似等。
- External influence. 天气条件、事件等。
2. Contribution
- 使用Conv来model任意两region之间的spatial dependencies.
- 使用3个ResNet来model temporal closeness, period和trend的temporal dependencies.
- Assigning different weights to aggregate 3 outputs of ResNet, and then aggregate external factors.
- Outperform 6 baselines on Beijing and NYC dataset.
3. Preliminaries
- Region. 将城市划分为grid map (Figure 2).
- Flow (2 channels). 归一化到[-1,1].

4. ST-ResNet (Figure 3)
- ST-ResNet
- Include temporal closeness (recent), period (near), trend (distant) and external 4个主要部分。
- Temporal closeness (recent), period (near), trend (distant)的ResNet结构相同,其中包含2个Conv和L个Residual (Figure 4). 由于地铁或高速公路会导致两个很远的region具有很强的关联性,因此使用具有层级性的stack Conv来实现,并利用residual的形式来提高stack Conv的收敛性。Relu之前增加了ReLU层。

- External通过两层FC. Regard as embedding layer + mapping layer (same shape as Xt).
- Fusion包含3个可学习的权重参数,乘以对应的3个ResNet输出后相加,其结果再与FC输出相加,经过tanh激活函数。


- MSE loss, Adam.

5. Algorithm
- p: one day.
- q: one-week.

6. DataSet (Table 1)
- TaxiBJ. Taxicab GPS and moteorology data. 选择最近4周作为testing data.
- BikeNYC. NYC Bike system. 选择最近10天作为testing data.

- (Figure 5) 假期和天气会影响北京办公区的流量。

- (Figure 6) recent时间段的相关性更大,办公区周末的流量较低,办公区流量呈现下降趋势,居住区呈现上升趋势。

7. Baseline
- HA. 历史inflow,outflow均值。
- ARIMA. Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average. 用于预测时间序列的值。
- SARIMA. Seasonal ARIMA.
- VAR. Vector Auto-Regressive(VAR), spatio-temporal model.
- ST-ANN. extracts spatial (nearby 8 regions’ values) and temporal (8 previous time intervals) features, then fed into an artificial neural network.
- DeepST. State-of-the-art. DNN for spatio-temporal data. 4 variants: DeepST-C, DeepST-CP, DeepST-CPT, and DeepST-CPTM. Focus on temporal dependencies and external factors.
8. Experiments
- Theano&Keras.
- Conv2: 2 filters.
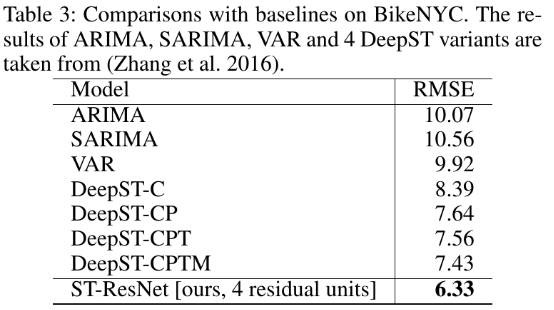
- Evaluation Metric: Root MSE.


9. Related Work
- Conv: capture spatial dependencies.
- RNN: capture temporal denpendencies.
- ConvLSTM: capture spatial and temporal denpendencies. But can not model very long-range temporal denpendencies(period and trend).
10. Future
Consider other types of flows: taxi, truck, bus, phone signal, metro card swiping.